Events
Prof. Fan Yihui And Prof. Mao Renfang of the School of Medicine And Their Teams Facilitae Functional Genomics Research by Developing Database Query System
On April 2, the research results of the database query system developed by Professor Fan Yihui and Professor Mao Renfang of the Medical School, Nantong University,was published online in a Chinese Journal of Immunology(English version),also a top immunology journal in China: Cellular & Molecular Immunology ( Impact Factor 8.2, Area 1, Chinese Academy of Sciences). The development of this system will greatly facilitate biologists to screen important DNA regulatory elements and help functional genomics research.
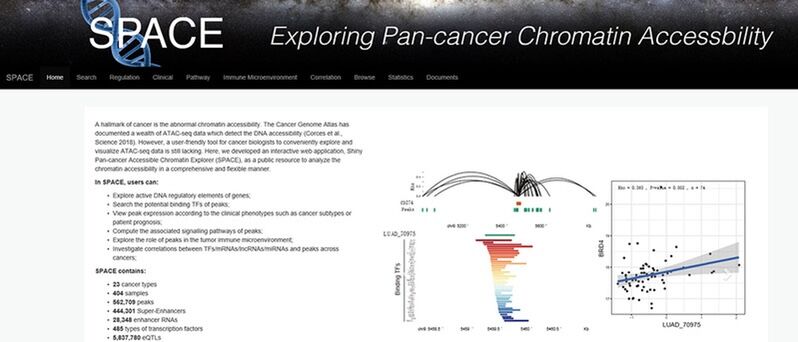
The human genetic material (genome) consists of approximately 3.16 billion base pairs in four kinds: A、T、C and G. The linear sequence of these base DNA chains is approximately 2m long and stored in nuclei with a diameter of only 5 microns by high-orderly assembly. Of these genetic materials, only less than 2% of DNA sequences can encode proteins. Over a long period of time, the DNA that do not encode proteins are called Junk DNA. However, there are more and more evidences indicating that these Junk DNA have important regulatory functions for spatiotemporal expression of genes, and are important regulatory elements to determine the cell fate. In comparison with the genes that have been studied and clearly labeled, the research on these Junk DNA is rather difficult. The accessibility of DNA, which is an important criterion to identify whether Junk DNA have functions, can be achieved by high-throughput sequencing techniques. Yet the unlabeled preliminary results of sequencing are difficult to be directly applied by scientists, thus greatly hindering subsequent functional studies.
To address this bottleneck in functional genomics research, a one-step query system (SPACE, http://fun-science.club/SPACE) was developed by the teams of Professor Fan Yihui and Professor Mao Renfang of School of Medicine. As with search for genes, researchers may query the relationship between DNA regulatory elements and gene expression, and the prognosis of tumor patients. The SPACE query system is the first data system in the world to directly query ATAC signals and tumor patients’ expression patterns as well as their prognosis. This system is successfully developed mainly by the undergraduate team of School of Medicine.